As most CIOs, cloud engineers, and 48% of IT decision-makers agree - unpredictable workload demands or rapid user base growth is one of the biggest challenges they face when dealing with server workload constraints.
Not being able to deal with the surges in demands or user base growth puts a question to business efficiency - which boils down to business loss/ gain.
Thanks to Cloud and its near infinite scale - enterprises and organizations can now align business capabilities to the cloud and experience signature advantages ranging from cost savings to flexibility.
Cloud as a storage solution is particularly a favorable solution to companies with growing pools of data and can expand to accommodate any IT scenario that’s imaginable. This scalability of cloud computing equips and powers businesses that experience sudden and unexpected spikes.
IT teams are required to architect applications to handle fluctuations in scale by proper capacity planning. They must plan and properly design the supporting infrastructure to ensure unused capacity isn’t idle, but available when needed. Below are a few ways of capacity planning to ensure you’re ready when spikes occur. .
Cloud scalability refers to a cloud service provider's (CSP) ability to increase or decrease the number of computing resources available to your application as per the demands.
There are several approaches to scale an application and its underlying architecture to accommodate capacity fluctuations. We must first outline the fundamental principles of cloud scaling in order to better understand how to handle unexpected scaling.
Let’s use an analogy. Assume your cloud environment as a bathtub. The basin is the resources available for hosting the application and the drain is the application’s performance i.e its ability to process the requests. Let’s say you turn on the faucet. In order to fill in more water, your drain must do the job of draining the water else it’s a mess.
It’s the same with your application. You need to process data as quickly as possible to avoid slowdowns. For that, it’s important to maintain an equilibrium of capacity and performance to meet the demands. When the load becomes too much, it could get difficult to recover without turning off the requests.
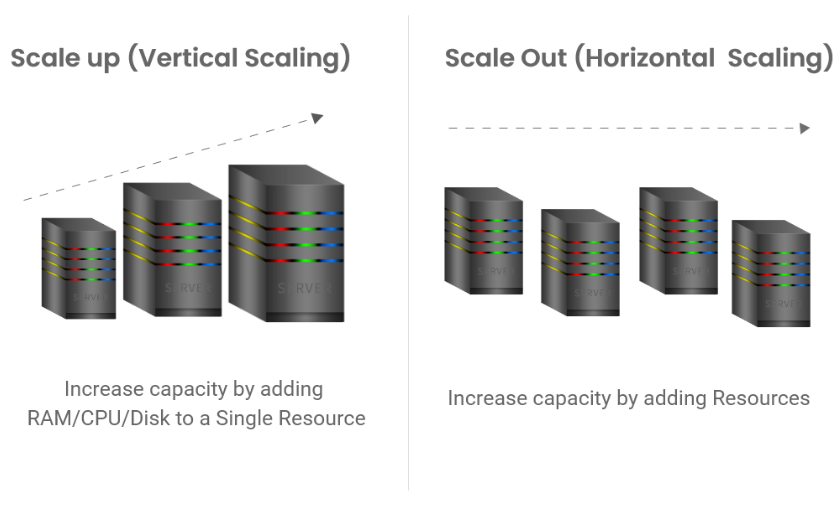
Cloud administrators can scale vertically to handle increased flow by adding more capacity to their VM. Vertical scaling, also known as "scaling up,” is adding more or faster CPUs, memory, or resources to an existing server or replacing it with a more powerful server. Though it addresses a consistent and predictable increase, it isn’t capable to addressing unpredictable spikes above the threshold. Considering our tub analogy, a larger basin does not necessarily solve the overflow problem; rather, it simply buys time.
Alternatively, you can scale your application horizontally. Also known as "scaling out," your application responds to increased traffic by adding more instances, or nodes, to your resource pool. This type of scaling works in distributed systems where load balancers typically are used to route traffic accordingly.
With vertical scaling, you may reach your limits of resource exhaustion – either financially or physically. But Horizonal scaling is a more effective way to solve the overflow problem with smaller, low-cost resources used in larger quantities.
A similar concept is Cloud Elasticity where the demands can be addressed dynamically.
Elasticity refers to a cloud's ability to automatically expand or compress infrastructure resources in response to a sudden increase or decrease in demand, allowing the workload to be managed efficiently. This is not applicable in all environments but is most useful in situations where resource requirements fluctuate dramatically over a short period of time.
Elasticity contributes to lower infrastructure costs and is not suitable in situations where a persistent resource infrastructure is required to handle a heavy workload.
It is most commonly used in public cloud pay-per-use services - where IT managers are willing to pay only for the time spent using the resources.
Determining how you meet your workload demands or userbase spike solely depends on a business case. There are several aspects to consider such as cost, resource allocation, capacity, and business vision to understand the right cloud solution for you.
Let’s say you have an online shopping site with a transaction workload that spikes up during a festive season. Spike in workload indicates a spike in resources. In order to handle this situation, cloud elasticity is a much better solution than cloud elasticity. At the end of the season, the deployed resources can be requested to be withdrawn. Elasticity meets the dynamic changes where resources need to increase or decrease. Scalability, on the other hand, is used to address the increase in workload in an organization.
Whether your company is growing vertically, horizontally, or diagonally, it's critical to understand how much those changes cost and how they add value to your bottom line.
You can get context around your cloud computing for each business unit as you scale with our experts. Maganti IT is focused on offering a wide range of application development services - from design to deployment. Specialists at Maganti IT have years of experience under their belts and are fully aware of what it takes to build innovative cloud solutions.
We accelerate innovation, intelligence, and value across enterprises by providing custom cloud services and solutions that future-proofs your business. Talk to our experts now!